A classic data engineering task is to connect different systems together, in this blog we will run through the process of setting up the intergration of Snowflake with an S3 bucket. This will enable us to populate our snowflake instance with the data which we have in an S3 bucket.
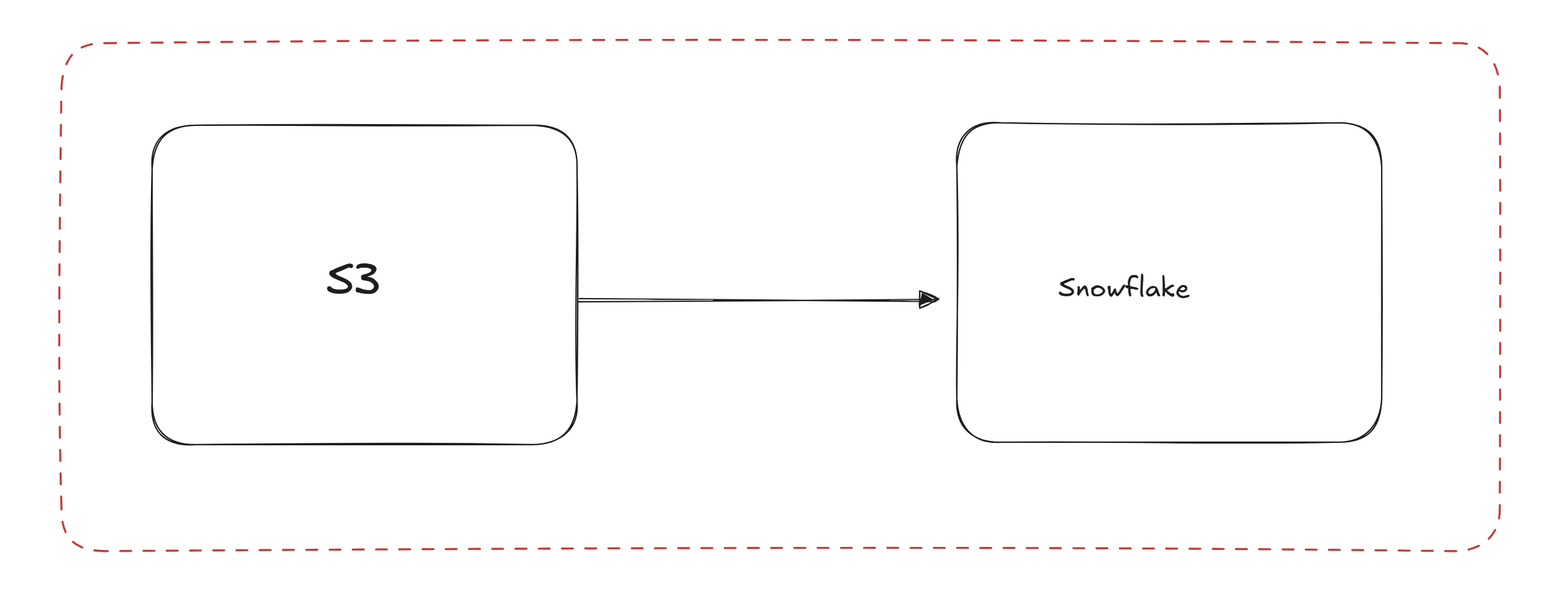
Why: S3 storage in AWS is exceptionally cheap so good for storing lots and lots of unstructured data. Snowflake is a very powerfull tool for transforming data so it makes sense as a palce to carry out our transformations.
Step 1 :We start off by setting up out our storage intergration.
CREATE or replace STORAGE INTEGRATION NAME_OF_INTERGRATION
TYPE = EXTERNAL_STAGE
STORAGE_PROVIDER = 'S3'
ENABLED = TRUE
STORAGE_AWS_ROLE_ARN = AWS_ARN_CODE
STORAGE_ALLOWED_LOCATIONS = ('s3://AWS_S3_BUCKET_NAME');
It should be noted that this occurs at a snowflake account level regardless of what data base and schema the Intergration is created in.
I think to think of storage intergration as the link between the two systems telling the snowflake side that it can go and get data out of a specific location.
Step 2
We need some of the information from the intergration to take back into S3 to set it up from the "other side"
We run the following command in snowflake.
DESC INTEGRATION Intergration name ;
This will give us a series of values in the results pane but we only need 2 of them
| STORAGE_AWS_EXTERNAL_ID ************** |
| STORAGE_AWS_IAM_USER_ARN *************** |
We can then go back and add these into the JSON of our IAM trust policy. Which will effectivly tell S3 that snowflake is allowed to come and communicate with the bucket.
Step 3
CREATE OR REPLACE FILE FORMAT "Name of file format"
TYPE = 'JSON'
STRIP_OUTER_ARRAY = TRUE;
Create a file format for what ever you expect to be ingesting. In our example we were using JSON files and we wanted to strip the outer layer but this would obviously depend on the file type which is applicable to your use case.
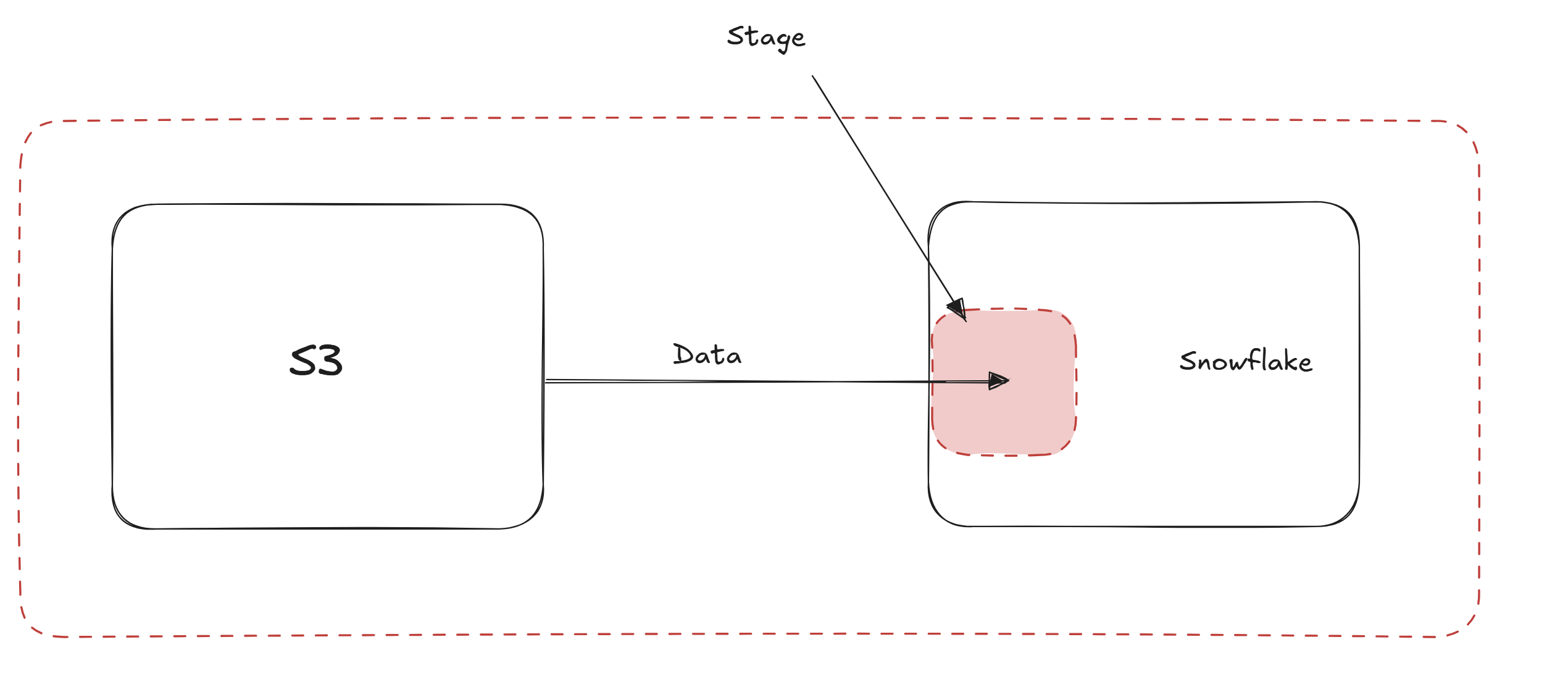
Step 4
CREATE OR REPLACE STAGE " Your Stage Name"
STORAGE_INTEGRATION = " Your Storage Intergration Name"
URL = " Link to the folder in your S3 bucket"
FILE_FORMAT = " Your File Format Name"
Create your stage in snowflake which will initially host your files.You also link it with your storage intergration. The stage is the place where the files will first be stored inside of snowflake when they are first brought in.
LIST @"your stage name";
List the stage name in order to make sure that it does indeed contain the correct files.
Step 5
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE "Your table name" (
json_data VARIANT)
Here we make a table in this case again we are creating a table with in single column, as we have a JSON file that we care going to parse at a later stage
Step 7
COPY INTO "Your table Name"
FROM @"Your stage name"
FILE_FORMAT = (FORMAT_NAME = "Your file format name");
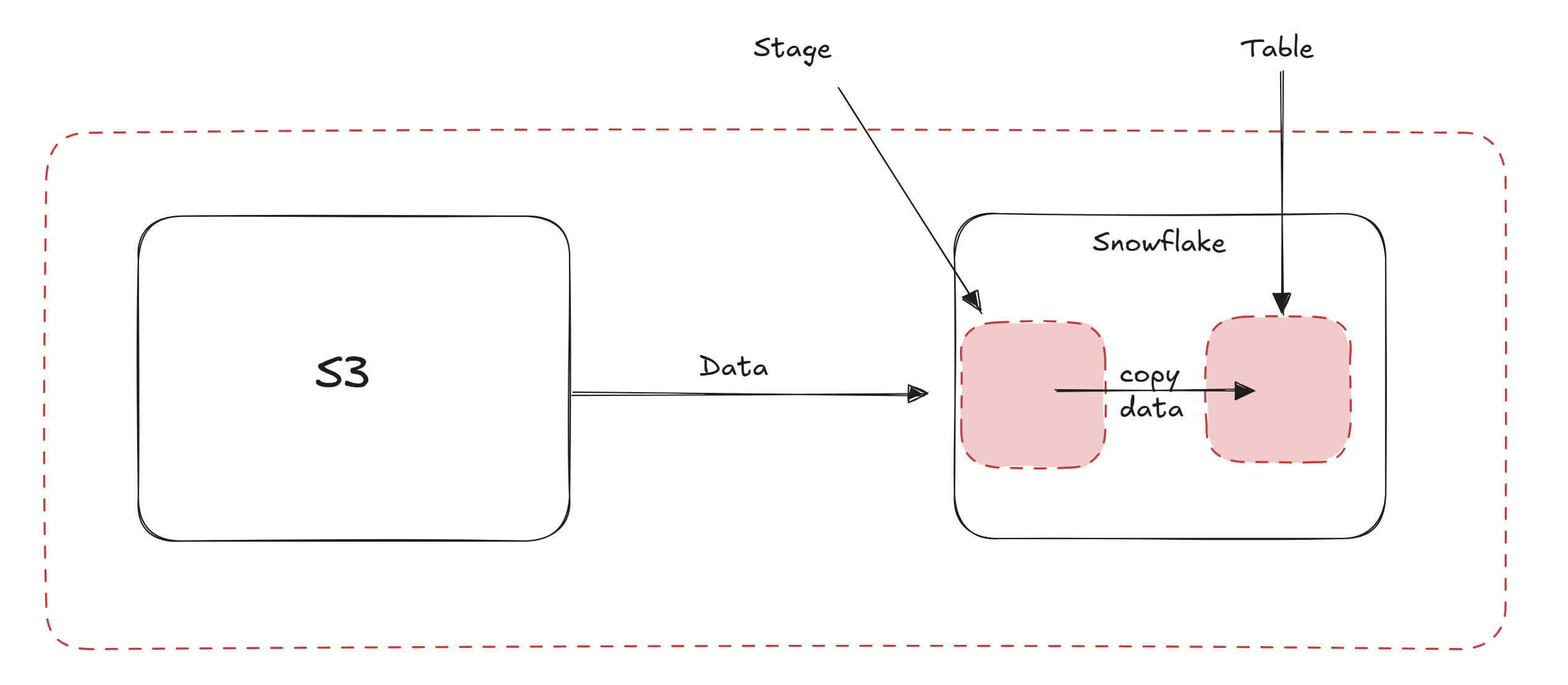
Here we are pushing from our stage into the the table using the previously created file format.
As a final check we may want to query the table which we have created in snowflake to ensure that we have the expected number and content of rows.
Future Steps
This can be considered out Bronze layer inside of snowflake, in a normal buissness scenario we would likely continue by parsing the Json inside of snowflake and enriching the data with buissness context, in what may be considered silver and gold layers. This may then be used for visualisations to allow the buissness to make decisions.
