I'd like to clarify what pivoting data from a wide format to a long format and vice versa are. This is best done with examples.
Pivoting from a wide format to a long format
In a wide format, data is spread across multiple columns. For example, the following is a sales dataset:
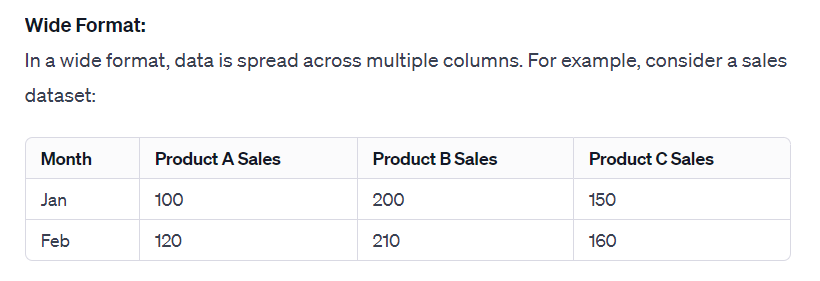
In a long format, the same data is condensed into fewer columns but it has more rows, making it easier to analyze certain types of data. In this case, they would be data of Product and Sales.
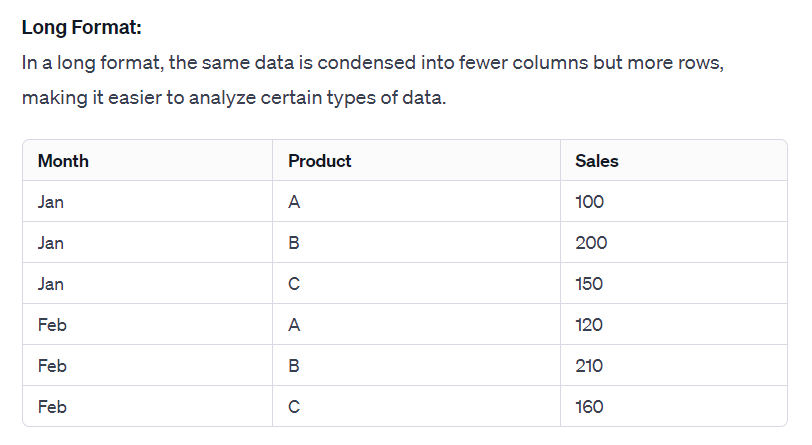
Pivoting to a long format is beneficial for performing certain types of analyses, such as time series analysis or comparison across different categories (in this case, products), as it aligns all data points of interest in a single column, making them easier to manipulate and analyze.
Pivoting from a long format to a wide format
In a long format, data is presented in a more stacked manner, as the following example shows:
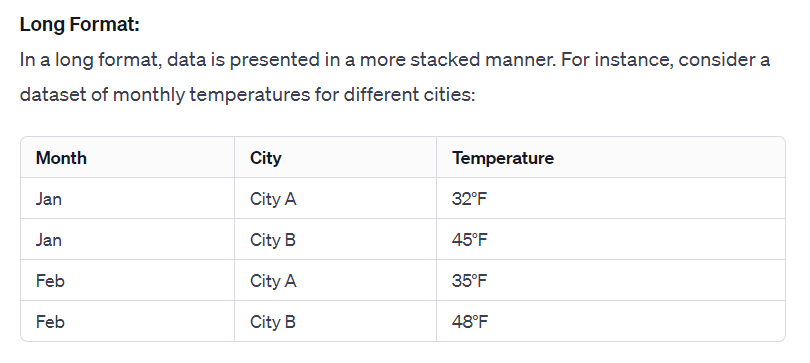
An example of a wide format:
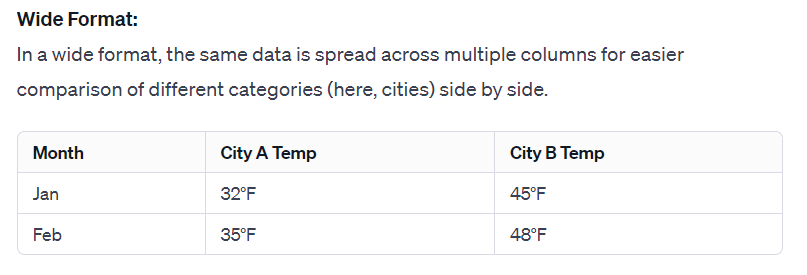
Pivoting to a wide format can make it easier to compare data across different categories (e.g., temperatures in different cities) in a side-by-side format, which is particularly use for identifying patterns or differences across categories.
